AWS Lambda: Synchronous or Asynchronous
Synchronous or Asynchronous?
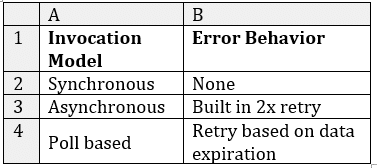
AWS Lambda Synchronous or Asynchronous – Synchronous Vs Asynchronous Error Behavior
Synchronous or Asynchronous Invocations are the 2 types of Invocations used by Lambda.
Upon executing code within Lambda, you may invoke your functions synchronously or asynchronously. They are both useful and required for various situations, but are accompanied with interesting side effects as well in your serverless space.
Synchronous functions:
– Utilized for discovering what the result of an operation is even prior to carrying on along to your next one.
– Simple just like invoking one function which performs a calculation and later on utilizes its result in the other function.
– Easier and simpler for handling and keeping track of since they mainly get invoked each one on its own after the other, in order.
– Provide you with the result of a function right before heading on to the following other one in order not to worry about getting any data missing.
At other times, it wouldn’t even matter what response you would get; it is simply satisfactory to discover your function has gotten fired and is now running perfectly well. In this case, you should rely on asynchronous functions for your invocations. An example of when its good for you to be choosing to run an asynchronous function is when you’d like to start a video encoding process. Lambda then sends a response stating that your video encoding function was invoked and has begun successfully. Since this function is asynchronous, you will receive this response right after the process starts, rather than needing to keep waiting up till the process finishes.
Functions that get invoked synchronously or asynchronously within Lambda get handled in various ways in case of failure, and this may inflict a couple of unexpected side effects in the logic of your program. In the case of synchronously invoking your functions directly, then the invoking application used will be held responsible for every single one of the retries. While relying on integrations you will find that they might include extra retries that come built in. Functions which get invoked asynchronously will not be relying on any invoking application for their retries, because the retries here will be built in and running automatically. The invocation shall get retried two times while having delays in-between. In case both retries end up in failure, the event will get discarded. Asynchronous invocations allow you to create a Dead Letter Queue that may be utilized for keeping the failing event from getting discarded. A Dead Letter Queue provides you with the opportunity to send unprocessed events to an Amazon SQSor SNS queue so that you get to build some logic to start dealing with.
Synchronous Invocation
Upon the invocation of a function synchronously, Lambda will run the function and await a response. Upon the finish of the function execution, Lambda will return a response from the function’s code holding extra data, like the executed function’s version. For invoking a function synchronously using the CLI, utilize the following command: invoke.
$ aws lambda invoke –function-name my-function –payload ‘{ “key”: “value” }’ response.json
{
“ExecutedVersion”: “$LATEST”,
“StatusCode”: 200
}
This below diagram displays the way clients invoke their Lambda functions synchronously. Lambda tends to send the events in a direct manner to your function and then starts sending the function’s response to its invoker.
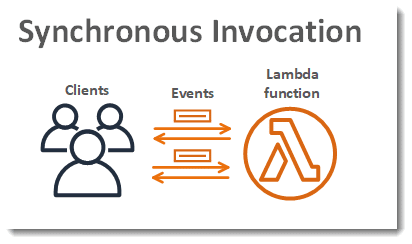
AWS Lambda Synchronous or Asynchronous – Synchronous Invocation
The payload refers to a string containing an event found in the JSON format. The file that get the response written by CLI from the function is called response.json. In the case of returning an object or error, the response will be that object or error sent in the JSON format. In case the function ends up exiting without error, its response will be null.
Output from command: shown in the terminal and contains data from headers found in the response coming from Lambda, including the version in which the event was processed (useful for aliases), and the status code which is sent back by Lambda. In case Lambda runs the function, 200 is what the status code will be, regardless if an error gets returned by the function.
In the case that Lambda fails to run the function, the error is going to get displayed in the output.
$ aws lambda invoke –function-name my-function –payload value response.json
An error occurred (InvalidRequestContentException) when calling the Invoke operation: Could not parse request body into json: Unrecognized token ‘value’: was expecting (‘true’, ‘false’ or ‘null’)
at [Source: (byte[])”value”; line: 1, column: 11]
Rely on the –log-type option for getting logs for your invocation coming from the command line. Included in the response is a LogResult field which has up to 4 KB of base64-encoded logs from that invocation.
$ aws lambda invoke –function-name my-function out –log-type Tail
{
“StatusCode”: 200,
“LogResult”: “U1RBUlQgUmVxdWVzdElkOiA4N2QwNDRiOC1mMTU0LTExZTgtOGNkYS0yOTc0YzVlNGZiMjEgVmVyc2lvb…”,
“ExecutedVersion”: “$LATEST”
}
It’s possible to utilize the base64 utility for decoding the logs.
$ aws lambda invoke –function-name my-function out –log-type Tail \
–query ‘LogResult’ –output text | base64 -d
START RequestId: 57f231fb-1730-4395-85cb-4f71bd2b87b8 Version: $LATEST
“AWS_SESSION_TOKEN”: “AgoJb3JpZ2luX2VjELj…”, “_X_AMZN_TRACE_ID”: “Root=1-5d02e5ca-f5792818b6fe8368e5b51d50;Parent=191db58857df8395;Sampled=0″”,ask/lib:/opt/lib”,
END RequestId: 57f231fb-1730-4395-85cb-4f71bd2b87b8
REPORT RequestId: 57f231fb-1730-4395-85cb-4f71bd2b87b8 Duration: 79.67 ms Billed Duration: 100 ms Memory Size: 128 MB Max Memory Used: 73 MB
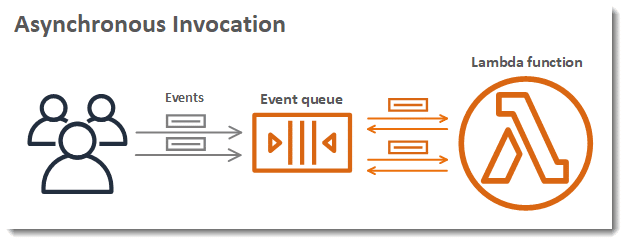
AWS Lambda Synchronous or Asynchronous – Asynchronous Invocation
Asynchronous Invocation
When a function is invoked asynchronously, waiting for a response to arrive from the function code is not necessary. The event gets handed off to Lambda and Lambda will be handling the rest. The way that Lambda handles errors may be configured, and it’s possible to send invocation records to reach a downstream resource for the sake of chaining together the components of your used application.
In the below diagram you can see clients invoking a Lambda function asynchronously. Lambda tends to queue its events prior to sending them to functions.
Asynchronous invocation:
The event gets placed by Lambda in a queue and then a success response is returned with absolutely no additional information. Another different process will be reading events from that queue and then sending them straight to your function. For getting a function invoked asynchronously, you must set the invocation type parameter to the following: Event.
$ aws lambda invoke –function-name my-function –invocation-type Event –payload ‘{ “key”: “value” }’ response.json{ “StatusCode”: 202}
Output file is (response.json) and it will not contain any kind of data, but it will still be created upon running this command. In case the event was not added by to the queue, the error message will be displayed in the command output.
Lambda manages the function’s asynchronous event queue and attempts to retry on errors. In case an error is returned, Lambda will run the function an extra 2 more times, while having to wait for 1 minute in between the first 2 attempts being made, and 2 minutes in between the 2nd and 3rd attempts made. Function errors will be including errors that get returned through the function’s code and errors that get returned through the function’s runtime, for example: timeouts.
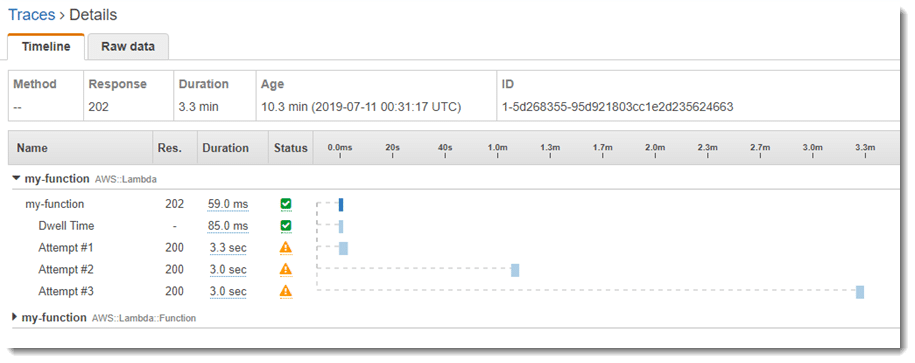
AWS Lambda Synchronous or Asynchronous – Error Behavior
In case the function did not include enough concurrency available for processing every single event, some additional requests will get throttled.
The below example displays an event which got successfully added to the queue, but remains pending for a whole one hour late because of throttling.
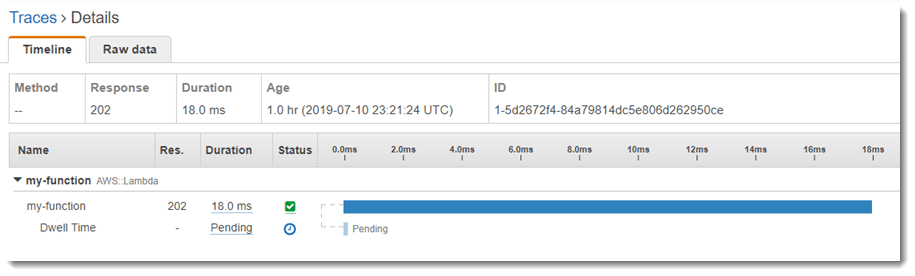
AWS Lambda Synchronous or Asynchronous – Error Behavior Pending
It’s also possible to get Lambda configured for sending an invocation record to a different service. The below destinations are supported by Lambda for asynchronous invocation.
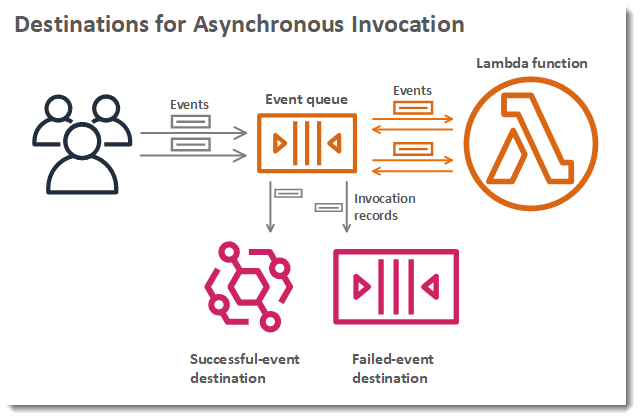
AWS Lambda Synchronous or Asynchronous – Destinations for Asynchronous Invocation
- Amazon SQS: queue.
- Amazon SNS: topic.
- AWS Lambda:
- Amazon EventBridge: event bus.
Invocation record:
– Includes detailed information regarding the request and response all in a JSON format. – It’s possible to get separate destinations configured for events which get processed in a successful manner, and the events which tend to fail every processing attempt.
– It’s possible to get an SQS queue or SNS topic configured as a dead-letter queue for an discarded event whatsoever.
– Lambda will merely be sending for dead-letter queues, the content of its events, with no details regarding the response.